 Transformer Gas Analysis refers to testing and interpreting the gases dissolved in transformer oil, known as Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA). It is one of the most important diagnostic tools for identifying incipient faults inside a transformer before a major failure occurs.
Transformer Gas Analysis refers to testing and interpreting the gases dissolved in transformer oil, known as Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA). It is one of the most important diagnostic tools for identifying incipient faults inside a transformer before a major failure occurs.
What Is Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA)?
When internal faults (like overheating, arcing, or insulation degradation) occur, they break down the oil and solid insulation, producing gases that dissolve in the oil. DGA tests detect and quantify these gases.
Key Gases Monitored in DGA
| Gas | Chemical | Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H₂ | Partial discharges, corona |
| Methane | CH₄ | Low-temp oil overheating |
| Ethane | C₂H₆ | Low-energy arcing or overheating |
| Ethylene | C₂H₄ | High-temp oil overheating |
| Acetylene | C₂H₂ | High-energy arcing |
| Carbon Monoxide | CO | Paper insulation degradation |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO₂ | Paper degradation (normal aging) |
| Oxygen & Nitrogen | O₂, N₂ | Air ingress (leaks or breathing) |
Common DGA Diagnostic Methods
1. Key Gas Method
-
Looks at the dominant gas or gases to classify fault type.
-
Example:
-
High H₂ → Partial discharge
-
High C₂H₂ → Arcing
-
High CO → Paper overheating
-
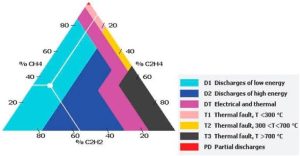
2. Duval Triangle Method
-
A graphical method using C₂H₂, C₂H₄, and CH₄ ratios.
-
Locates the type of fault (e.g., PD, arcing, thermal faults) within a triangle diagram.
3. Rogers Ratio Method
-
Uses ratios of key gases to determine fault type.
-
Example Ratios:
-
CH₄/H₂
-
C₂H₂/C₂H₄
-
C₂H₄/C₂H₆
-
4. IEC 60599 & IEEE C57.104 Guidelines
-
Provide gas limits, interpretation rules, and fault classification.
DGA Best Practices
-
Take oil samples annually or semi-annually for critical transformers
-
Perform DGA after any fault, protection trip, or suspected overheating
-
Combine DGA with furan analysis (for paper aging) and BDV tests
Typical DGA Report Includes:
-
Individual gas concentrations (ppm)
-
Total Combustible Gas (TCG)
-
Key ratios (Rogers, Duval inputs)
-
Fault classification
-
Trend graph of gas over time

